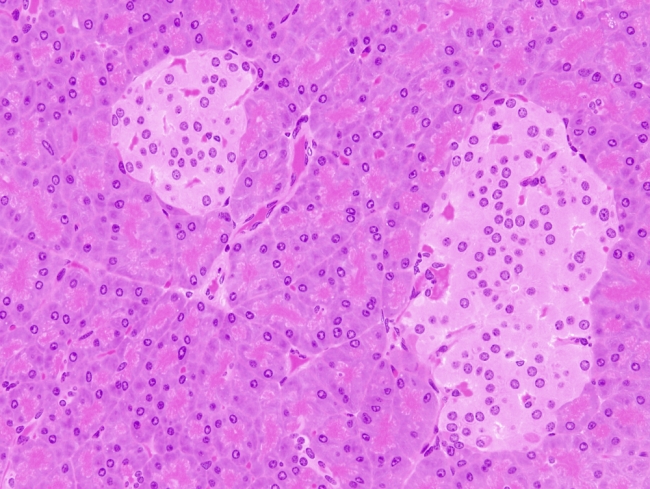
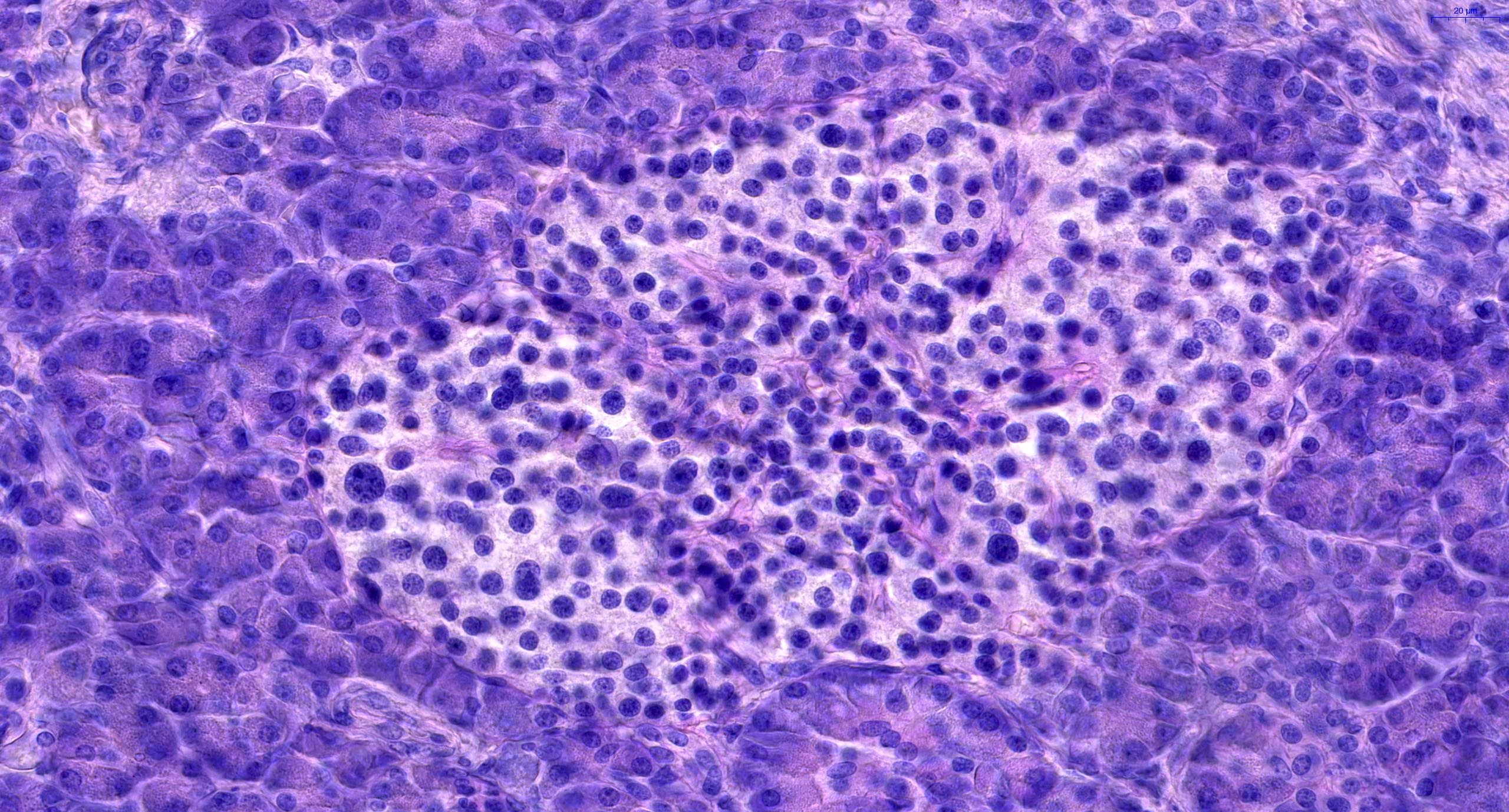
The endocrine component of the pancreas consists of the islets of Langerhans, the round masses of glandular epithelial cells appearing as nodules in the endocrine pancreas The cells are found in irregular cords and clumps, as opposed to the neighboring, highly organized aciniThe pancreas is formed from two basic tissue types termed the exocrine and endocrine pancreas Although the exocrine and endocrine pancreas share a similar anatomic location, for all intensive purposes they are histologically and physiologically distinct So too are the pathological processes which affect themUse examples of the secretory products to explain
Liver And Pancreas
Exocrine and endocrine pancreas histology
Exocrine and endocrine pancreas histology- The pancreas is a twoheaded organ, not only in origin but also in function In origin, the pancreas develops from two separate primordia In function, the organ has both endocrine function in relation to regulating blood glucose (and also other hormone secretions) and gastrointestinal function as an exocrine (digestive) organ, see exocrine pancreas Histology of the exocrine pancreas Pietro M Motta Corresponding Author Department of Anatomy, University of Rome La Sapienza, I‐ Rome, Italy Distribution of neuropeptides in endocrine and exocrine pancreas of longlegged buzzard (Buteo rufinus) An immunohistochemical study, Regulatory Peptides, /jregpep7, 166



Functional Anatomy Of The Endocrine Pancreas
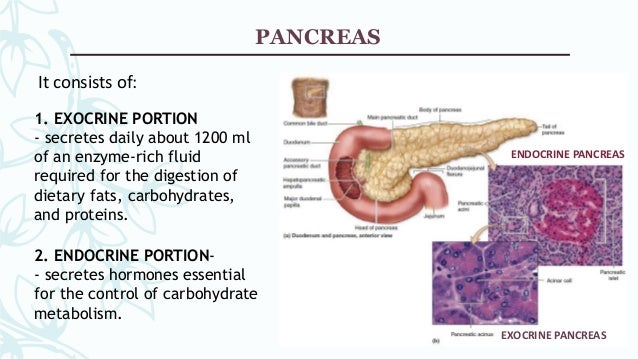
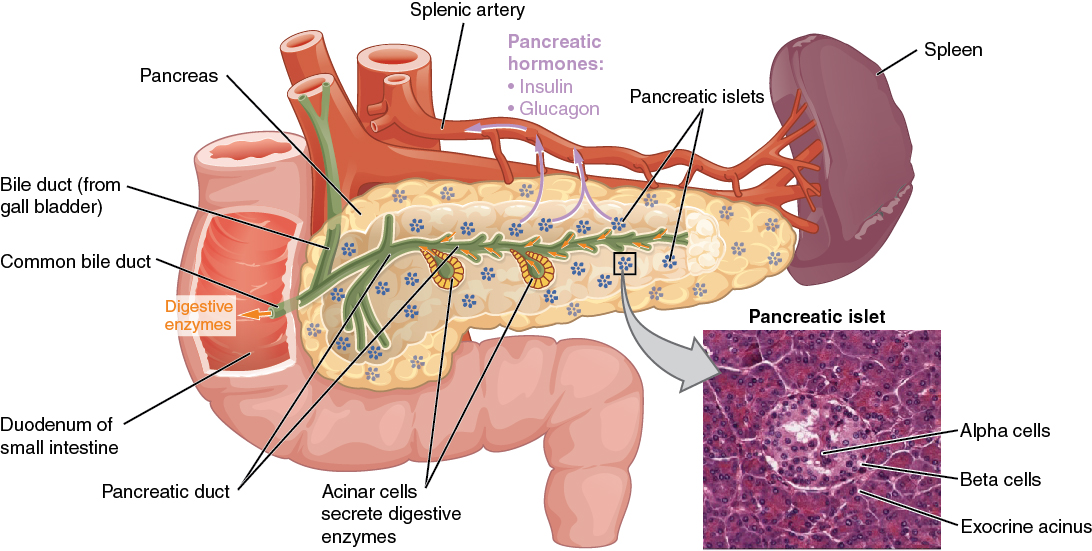
The pancreas is the main enzyme producing accessory gland of the digestive system It has both exocrine and endocrine functions Exocrine Pancreas The exocrine part of the pancreas has closely packed serous acini, similar to those of the digestive glandsThe pancreas is a long, slender organ, most of which is located posterior to the bottom half of the stomach (Figure 1791)Although it is primarily an exocrine gland, secreting a variety of digestive enzymes, the pancreas also has endocrine cells Its pancreatic islets—clusters of cells formerly known as the islets of Langerhans—secrete the hormones glucagon, insulin, somatostatin, and The pancreas is both an exocrine accessory digestive organ and a hormone secreting endocrine gland The bulk of the pancreatic tissue is formed by the exocrine component, which consists of many serous pancreatic acini cells These acini synthesize and secrete a variety of enzymes essential to successfully "rest and digest"
Pancreatic Exocrine Tumors About 94% of pancreatic cancers are classified as exocrine tumors These tumors start in the exocrine cells of the pancreas The following table describes the most common pancreatic exocrine tumors Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of pancreatic cancer It accounts for about 90% of all pancreatic cancersThe pancreas is a large gland that has both exocrine and endocrine functions The majority of the pancreas consists of exocrine glands that produce about 15 liters of alkaline digestive enzymes daily, which is secreted directly into the duodenumDistinguish between the exocrine and endocrine secretions of the pancreas a The exocrine pancreas produces bile and the endocrine pancreas concentrates and stores bile b The exocrine pancreas produces acidic secretions and the endocrine pancreas produces alkaline secretions c The exocrine pancreas produces mucous and the endocrine
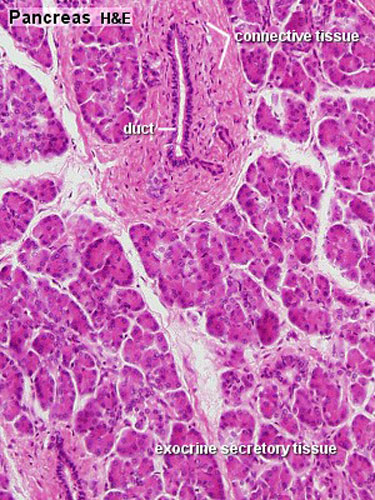
Kamyar M Hedayat, JeanClaude Lapraz, in The Theory of Endobiogeny, 19 Abstract The exocrine pancreas is a gland that produces digestive enzymes and bicarbonate It is an essential organ for the survival, adaptation, and restoration of the organism The exocrine pancreas' function must be evaluated in relationship to the endocrine pancreas, stomach, intestines, liver,Functioning as an exocrine gland, the pancreas excretes enzymes to break do View the full answer Transcribed image text Question 62 3 pts Why is the pancreas both an exocrine and an endocrine gland?The pancreas is divided into lobules by connective tissue septae Lobules are composed largely of grapelike clusters of exocrine cells called acini, which s



Histology Home Page




Pancreas Histology Osmosis
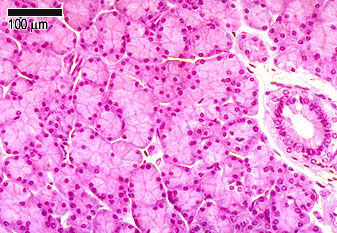
Start studying Physiology Lecture 21 & 22Endocrine Pancreas and Diabetes Mellitus Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools exocrine and endocrine exocrine gland of the pancreas Histology Overview forThe endocrine pancreas that secretes insulin and glucogon is more lightly stained and its cells cluster to form the Islets of Langerhans The rest of the image consists of the exocrine pancreas that produces several enzymes critical for digestion and adsorption of food Note how the cells of the exocrine pancreas form small clusters or aciniThe ducts that drain them secrete alkaline fluid • Clusters of endocrine cells, called Islets of Langerhans, secrete hormones that regulate blood glucose metabolism Key Anatomical & Histological Features The pancreas is lumpy and



Histology Of The Pancreas Springerlink
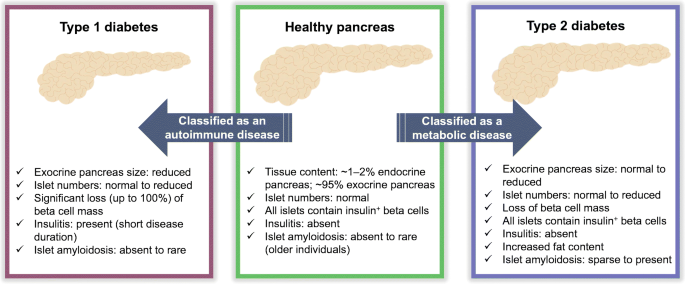



Organisation Of The Human Pancreas In Health And In Diabetes Springerlink
The term "endocrine" implies secretion into the internal milieu of a multicellular organism In contrast to exocrine tissues, where the secretory products are discharged into the external space the outer surface of the body, mucosal surfaces, duct systems the endocrine organs and cells secrete their products into the vascular systemPancreas Has both exocrine and endocrine functions • Most of the pancreas comprises exocrine cells, called acini, that secrete digestive enzymes; Exocrine part of the pancreas Histologically, the exocrine part of the pancreas shows the typical structure of the serous gland and represents roughly 98% of the organ's tissue The acini consist of strong basophilic cells, which contain numerous secretory granules Acini are made of zymogenic cells that surround a central lumen and are arranged in lobules




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia




Pancreas Histology Draw It To Know It
The pancreas contains two distinctive types of glandular tissue, an exocrine component and an endocrine component, which allow the organ to perform two different functions Exocrine glands secrete their products into a duct system The ducts, in turn, transport these secretions to a specific target Acini are the functional units of theAn essential pancreatic function is the conversion of food into fuel for the body's cells The exocrine part produces mainly digestive enzymes and helps in digestion, whereas the endocrine part is responsible for the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism (ie blood In pancreas histology of animal, you will find the both endocrine and exocrine parts The exocrine part forms the major portion of pancreas and consists of closely packed serous acini with zymogenic cells Again, the endocrine part consists of pancreatic islets of Langerhans which is located within the masses of serous acini
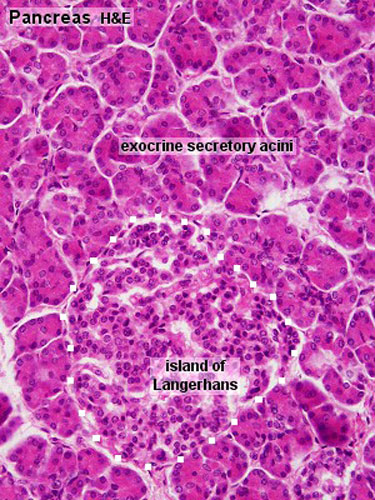



Gastrointestinal Tract Pancreas Histology Embryology




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
Pancreatic Histology Overview;Pancreas histology Review development of the pancreas In the 4th week 2 outpocketings of the endodermal lining of the duodenum develop as ventral and dorsal pancreas Ventral pancreas forms head and associates with common bile duct WhenPancreas The pancreas is located under the stomach and close to the upper small intestine (duodenum) It looks like 'knobby' tissue In addition to its endocrine function the pancreas is an exocrine organ The exocrine function involves producing digestive enzymes released into the small intestine We make more digestive enzymes than



Ha 235 Histology Accessory Digestive Glands




Exocrine And Endocrine Pancreas
Histologically, the exocrine pancreas closely resembles the salivary glands However, unlike the salivary glands, the pancreatic exocrine glands lack myoepithelial cells in the acini and do not possess striated ducts Additionally, centroacinar cells areThe exocrine pancreas contains lobular arrays of acini The acinar secretions of the exocrine pancreas are collected by the pancreatic ducts The ducts are surrounded by a small amount of connective tissue without inflammation or fibrosis (scarring)The endocrine pancreas resides in the islets which are regularly arranged and present within theEvent Details Meeting Objectives The goal of this 15day workshop will be to gather clinical and basic science investigators who are interested in diseases of the exocrine and/or endocrine pancreas and in achieving an understanding of how the two compartments interact in disease



Liver And Pancreas
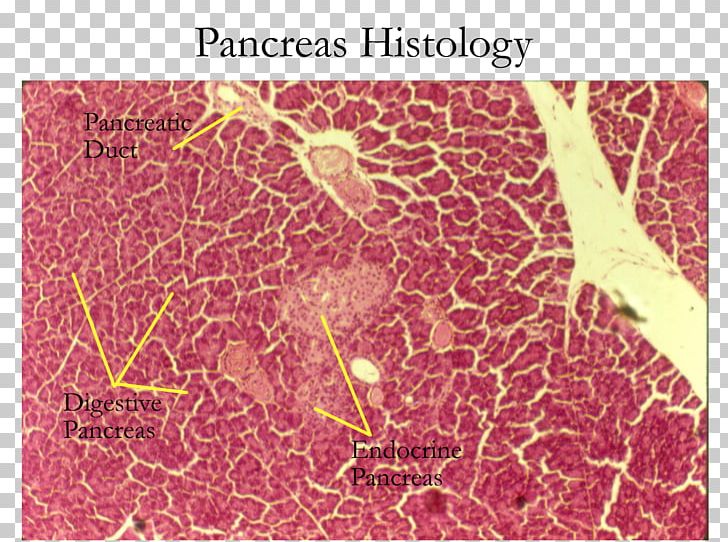



Exocrine Gland Pancreas Histology Endocrine Gland Endocrine System Png Clipart Acinus Blood Vessel Duct Endocrine Gland
Pancreas The pancreas is a lobulated and encapsulated gland composed of two functionally and histologically distinct components exocrine and endocrine In domestic species such as dogs and cats, the pancreas is a discrete organ directly adjacent to the duodenum, containing a right (proximal to the duodenum) and left limbPancreapedia, islet, Introduction The mandate for this chapter is to review the anatomy and histology of the pancreas, So Pancreas histology Exocrine & endocrine parts, Low blood glucose levels stimulate the release of glucagon, and these associated structures are known as the pancreatic acini, Diabetes and Pancreatic CancerA brief review of the normal histology of the pancreas, as presented by the URMC Pathology IT Program



Functional Anatomy Of The Endocrine Pancreas




01 07 15 Histology Of Tongue Liver Pancreas
The exocrine pancreas has a circular relationship with the endocrine pancreas The greater the hydrolysis and dispensation of nutrients by the exocrine pancreas is, the greater will be the solicitation of endocrine pancreatic hormones to regulate the distribution of these nutrientsSome glands retain their continuity with the surface via a duct and are known as EXOCRINE GLANDS Other glands lose this direct continuity with the surface when their ducts degenerate during development These glands are known as ENDOCRINE glands show labels This is the parotid gland, a type of salivary gland Exocrine vs Endocrine Fundamentally, the difference between exocrine and endocrine is exocrine secretes (via ducts) to an external surface or body cavity endocrine secretes within an enclosed system eg the bloodstream As the acini of the pancreas secrete into a network of ducts, this gives this organ an exocrine function



Animal Tissues Epithelium Pancreas Exocrine And Endocrine Gland Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology



Pituitary Gland
Histology serous ductal / acinar (exocrine cells) gland with tubuloalveolar arrangement with interspersed islets of Langerhans (endocrine cells) Terminology Anatomically, from right to left, the pancreas is divided into the caput (head), collum (neck), corpus (body) and cauda (tail) Pancreatic secretion is drained by the main pancreatic duct We can divide the pancreas into an exocrine gland, containing the acinar and duct tissue, and the endocrine gland containing the islets of Langerhans The majority of the pancreas is made up of the exocrine portion (85% by mass) and secretes digestive enzymes, water and bicarbonate to assist in digestionPancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue The pancreas is surrounded by a very thin connective tissue capsule that invaginates into the gland to form septae, which serve as scaffolding for large blood vessels Further, these septae divide the pancreas into distinctive lobules, as can clearly be seen in the image of mouse pancreas below (H&E)
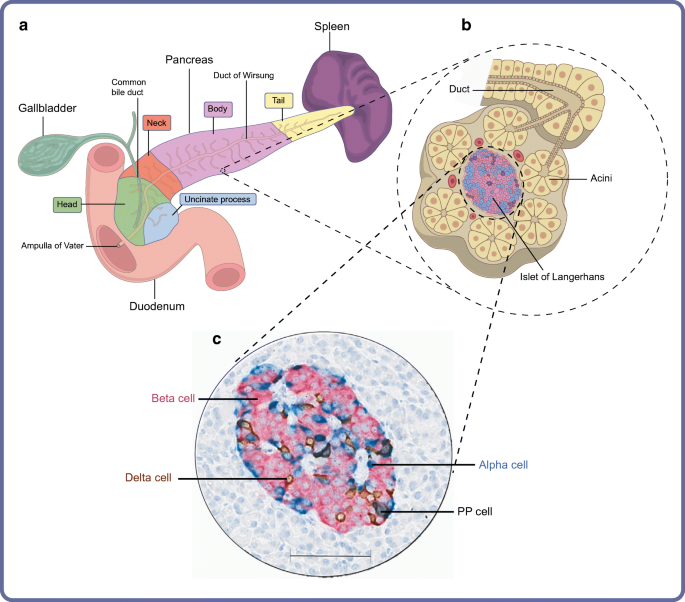



Organisation Of The Human Pancreas In Health And In Diabetes Springerlink




Pancreas Histology
Histology At the histological level the pancreas is made up of compound glands in "bunch of grapes" fashion The pancreas has an exocrine and endocrine component The exocrine compnent is demonstrated above in 3D with acini in "cluster of grapes" formation subtended by a duct Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD a06Fig 1 Pancreas, Human, (H & E) IL, Islets of Langerhans Examine a sample of pancreatic tissue with the 4X objective and identify the exocrine and endocrine portions of the pancreas The endocrine portion of the pancreas consists of islands of endocrine cells called the Islets of Langerhans (IL) The number of islets present in your section Although the exocrine and endocrine pancreas share a similar anatomic location, for all intensive purposes they are histologically and physiologically distinct So too are the pathological processes which affect them The exocrine pancreas is architecturally analogous to salivary glands with a highly branched and lobulated ductal system that terminates in secretory




Men1 Maintains Exocrine Pancreas Homeostasis In Response To Inflammation And Oncogenic Stress Pnas



Digestive The Histology Guide
The pancreas is both an exocrine (compound acinar) and an endocrine (islets of Langerhans) gland The exocrine pancreas releases alkaline secretions, containing enzymes, into the duodenum that aid in food digestion and neutralize the acidity of chyme leaving the stomach The islets synthesize hormones that regulate blood glucose levels 40xAnimal tissues Glandular epithelium PANCREAS Serous acini Islets of LangerhansTasks Overview of exocrine and endocrine pancreas Identify pancreatic acini with centroacinar cells Find intercalated duct and interlobular ducts Examine slide 1 at the lowest power and note that most of the section appears purple or bluish This is the parenchyma (or functional tissue) of the exocrine pancreas



Glandular Tissue The Histology Guide




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
Pancreas The pancreas is both an exocrine and an endocrine gland The endocrine pancreas consists of accumulations of palestaining cells called islets of Langerhans, which are surrounded by pancreatic acini The islet is composed of different populations of cells that secrete insulin, glucagon, somatostatin or pancreatic polypeptideEndocrine pancreas in cystic fibrosis an immunohistochemical study Hum Pathol 1984 Mar;15(3) 274 doi patients with cystic fibrosis in the latter part of the first decade of life have classic fibrocystic changes of the pancreas, with some persisting exocrine tissue, islets that appear normal, and prominent nesidioblastosis The latter




Pancreas Sciencedirect



Endocrine System Pns



Gastrointestinal Tract Pancreas Histology Embryology



Pathology Outlines Anatomy Histology
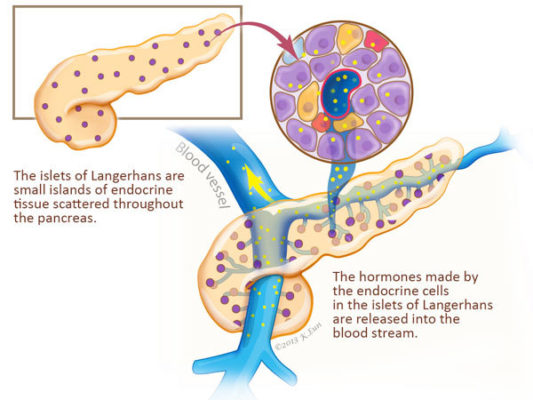
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/islets-of-langerhans/AThA8VjrhZ5mqO5a1ow4BQ_Islets_of_Langerhans.png)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/pancreatic-lobule/b6EWqkUnWbLMWLsNJApg_Pancreatic_lobule.png)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub



Structural Abnormalities In Islets From Very Young Children With Cystic Fibrosis May Contribute To Cystic Fibrosis Related Diabetes Scientific Reports




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia



Liver And Pancreas




Pancreas Objectives The Student Should Be Able To Describe 1 The Endocrine Part Of The Pancreas Within The Exocrine Part 2 The Histological Features Ppt Download



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue




Morphological Histological And Ultrastructural Studies On The Exocrine Pancreas Of Goose Sciencedirect




Pancreas Wikipedia




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia



Digestive The Histology Guide




Microphotograph Illustrate The Endocrine And Exocrine Portions Of Download Scientific Diagram



Histology Gallbladder And Pancreas




Pancreatic Tumors Vca Animal Hospital




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia




Exocrine Pancreas Flashcards Quizlet




Histology Of Mouse Pancreas Stained By Hematoxylin Eosin Normal Download Scientific Diagram



Pancreas Endocrine And Exocrine Functions Medical Library




Jci Abnormal Endocrine Pancreas Function At Birth In Cystic Fibrosis Ferrets




Pdf Histology Of Endocrine Pancreas In The Chabro Chicken Semantic Scholar



1



Dictionary Normal Pancreas The Human Protein Atlas



Pancreas Function Pancreatic Cancer Johns Hopkins Pathology




Pancreas Sciencedirect




Anatomyforme Endocrine Histology Pancreas Thymus And Pineal Body
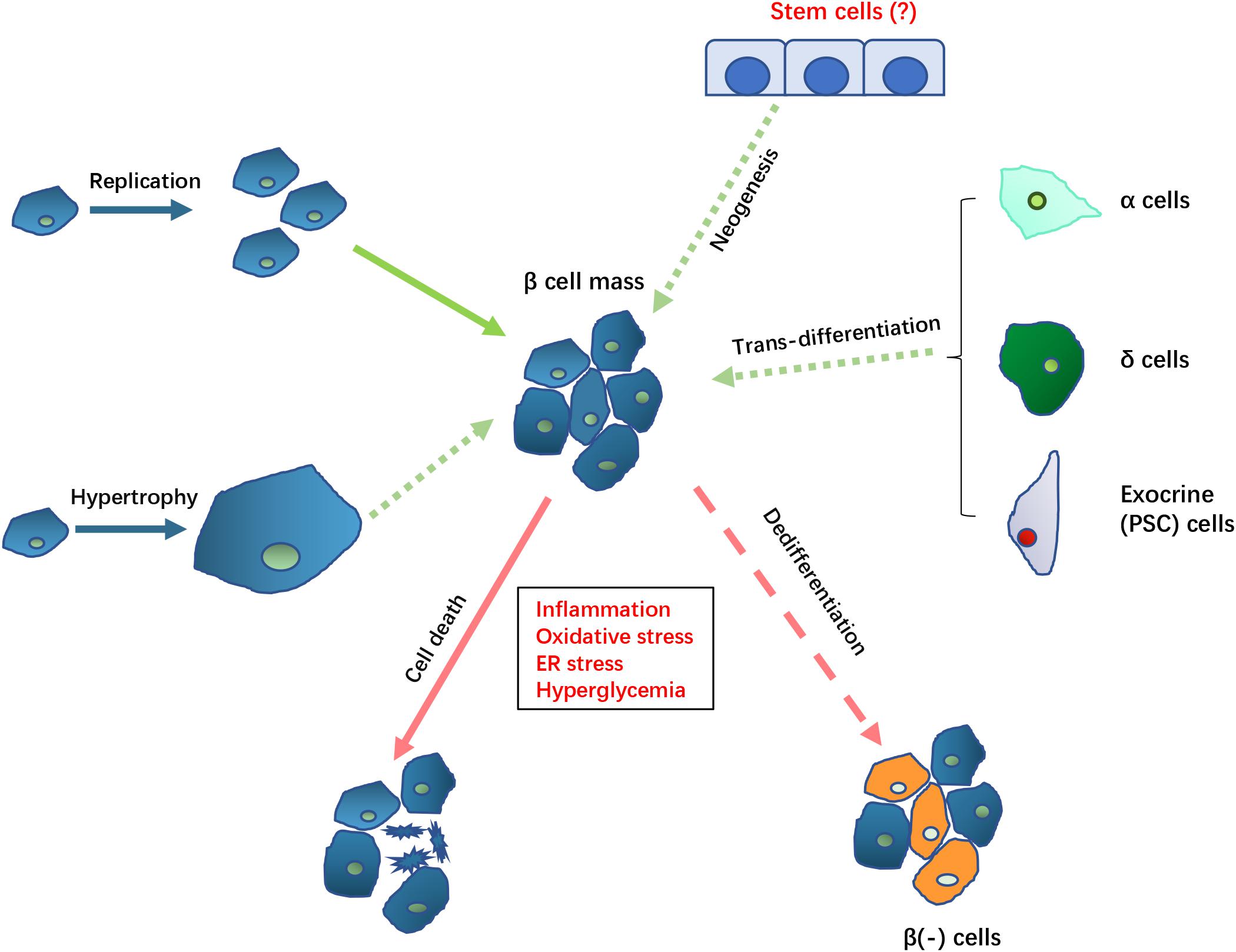



Frontiers Pathological Mechanisms In Diabetes Of The Exocrine Pancreas What S Known And What S To Know Physiology



Gross And Microscopic Anatomy Of The Pancreas



Endocrine Pancreas




Pancreatic Histology At The End Of Experimental Period Endocrine Download Scientific Diagram
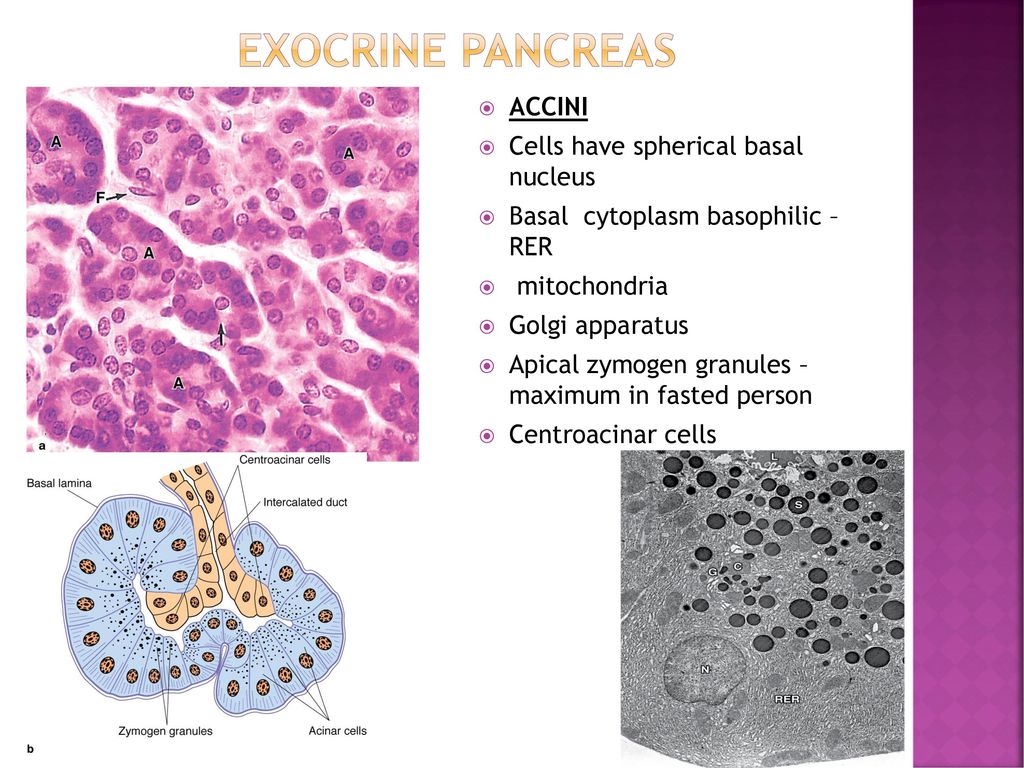



Histology Of Pancreas Ppt Download




Histoquarterly Pancreas Histology Blog
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/pancreas-histology/VMvxP28VGT55N9WvU3WgQ_mbuhIx2qC3HVaYNH69w_Body_of_Pancreas.png)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub




File 2424 Exocrine And Endocrine Pancreas Jpg Wikimedia Commons




01 07 15 Histology Of Tongue Liver Pancreas



Pathology Outlines Anatomy Histology




Department Of Pathology Ppt Video Online Download



1




The Endocrine And Exocrine Pancreas Cross Section Human P Flickr




Pancreas Histology Identifying Features With Labeled Slide Images Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia




Endocrine Pancreas Development In Growth Retarded Human Fetuses Diabetes



Pancreatic Histology Endocrine Tissue




Comparison Of Marmoset And Human Endocrine And Exocrine Pancreatic Download Scientific Diagram



Chapter 16 Page 3 Histologyolm




Pancreas Histology Osmosis



Labeled




Endocrine Pathology
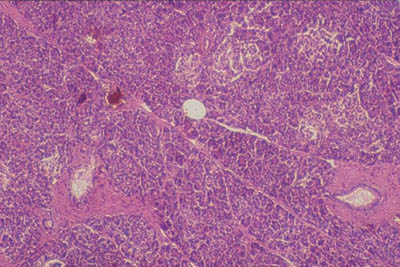



Histology World Histology Fact Sheet Pancreas
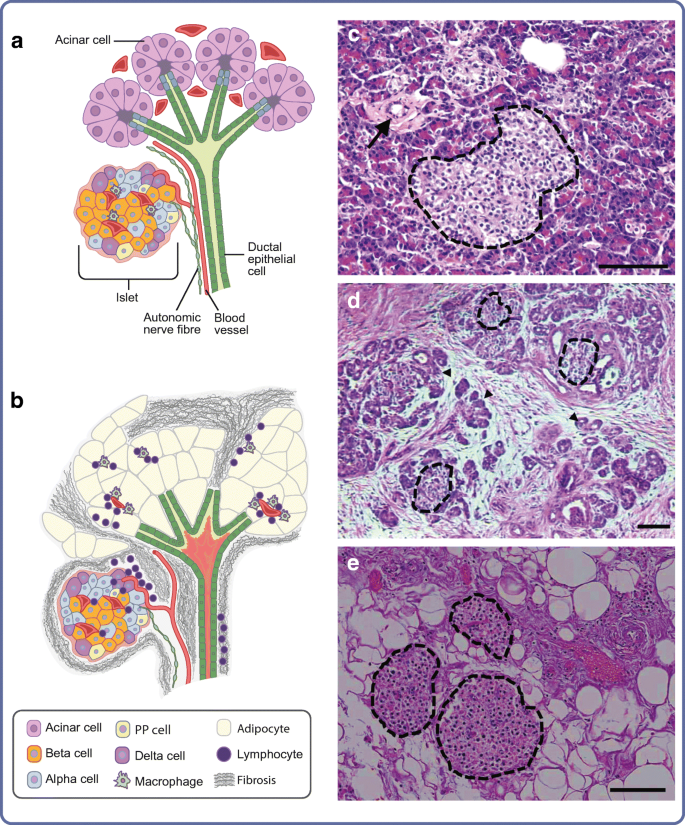



A Tale Of Two Pancreases Exocrine Pathology And Endocrine Dysfunction Springerlink
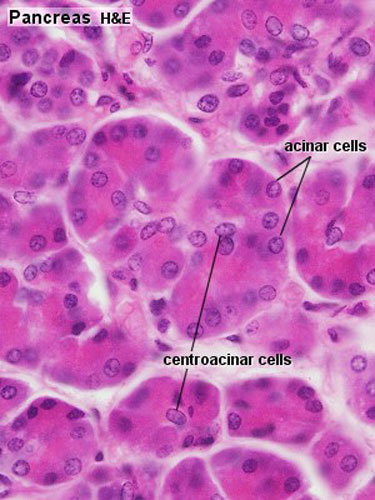



File Pancreas Histology 002 Jpg Embryology




Histological Section Of The Pancreas Courtesy Www Webanatomy Net Download Scientific Diagram
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1059/SXYoNKo9I26Aroj0YPbuHg_pancreatic-duct-system_english.jpg)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub




Human Pancreatic Afferent And Efferent Nerves Mapping And 3 D Illustration Of Exocrine Endocrine And Adipose Innervation American Journal Of Physiology Gastrointestinal And Liver Physiology




Histoquarterly Pancreas Histology Blog
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/pancreatic-acini/M2LWbCSc8l4TbZ24lNYg_Pancreatic_acinus.png)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub




Pancreas Sciencedirect
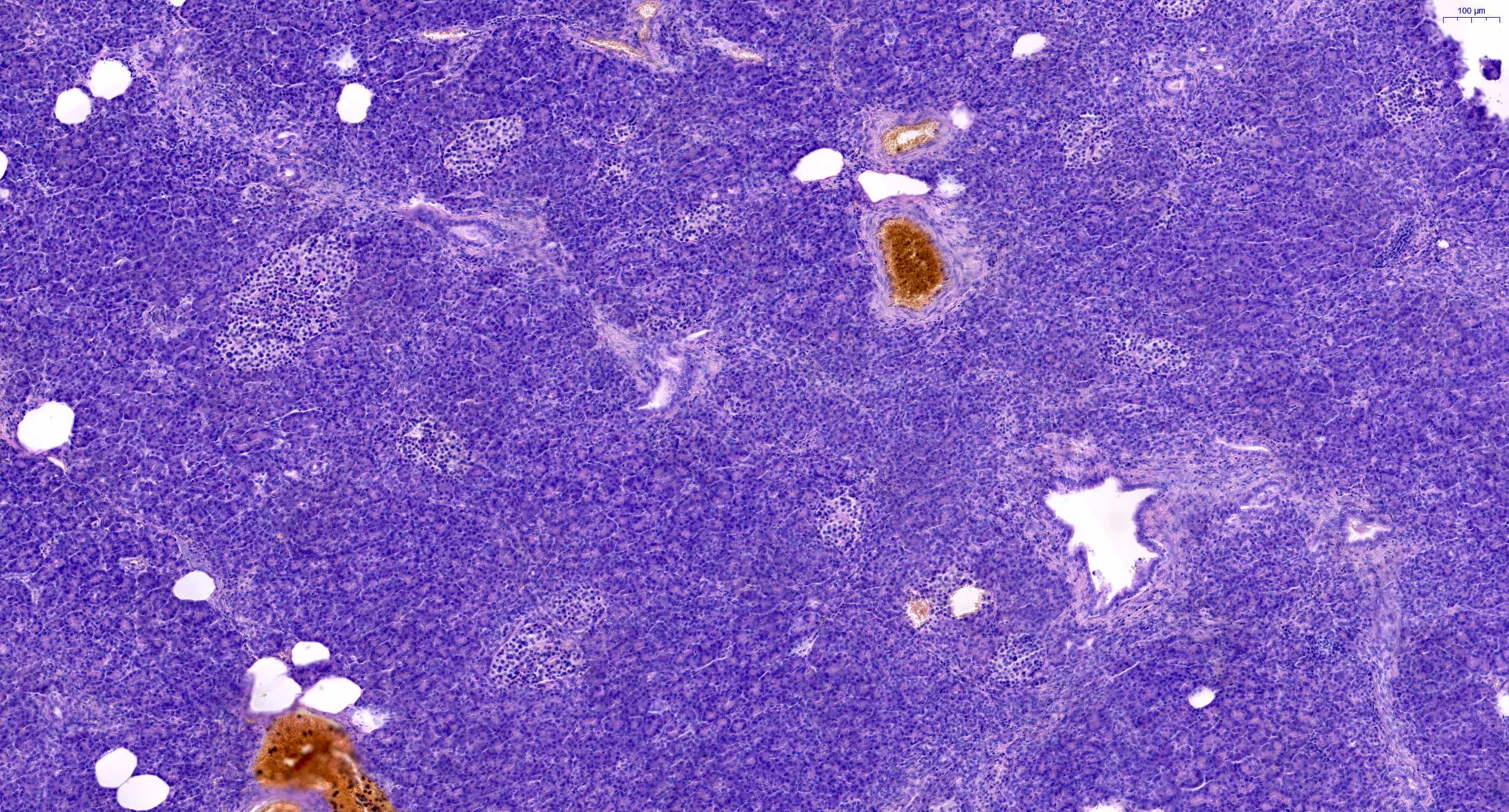



Pathology Outlines Anatomy Histology



Chapter 16 Page 3 Histologyolm




Pancreas Histology Flashcards Quizlet
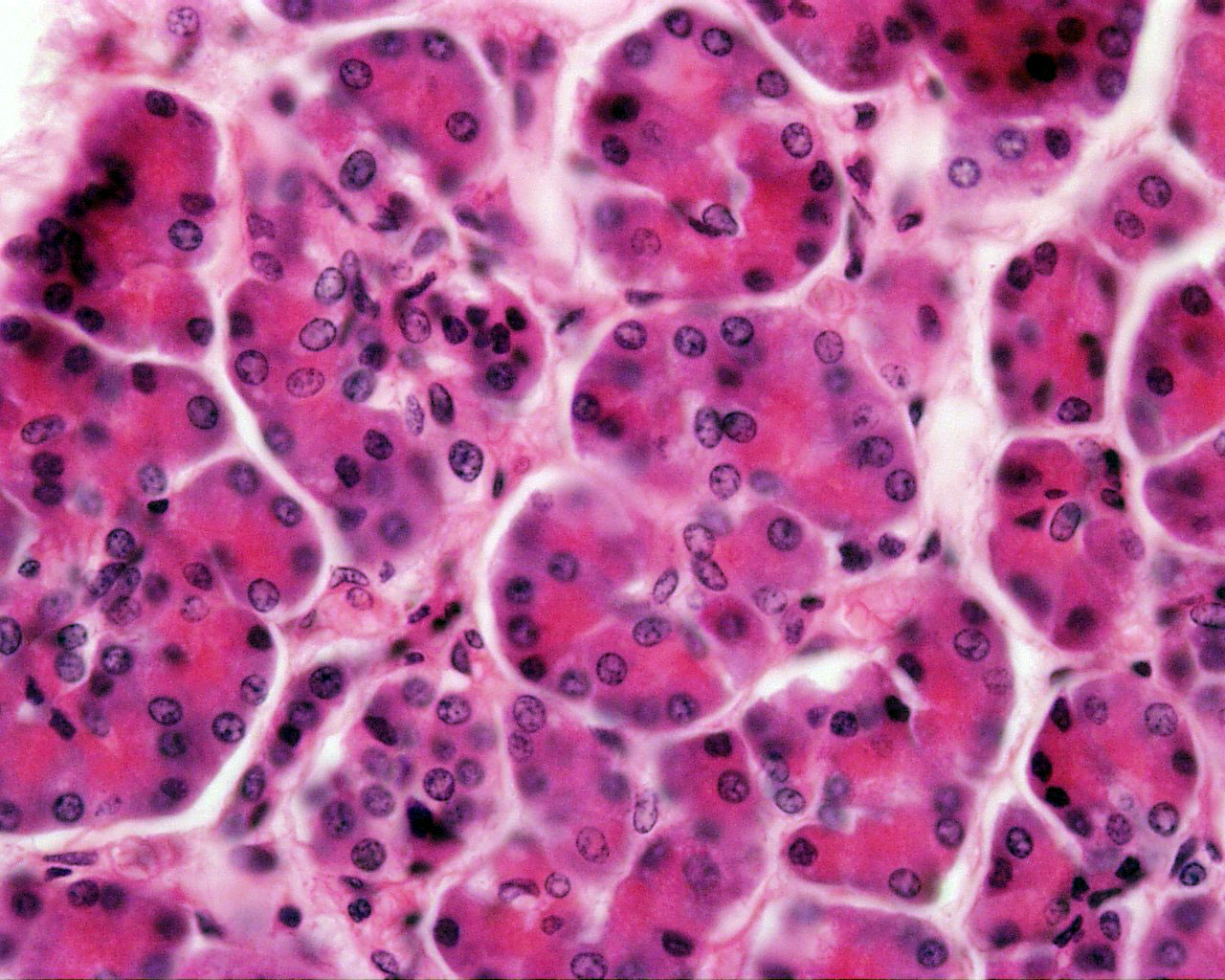



File Pancreas Histology 102 Jpg Embryology



Pancreatic Histology Endocrine Tissue



Normal Pancreas Pancreas Org
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1881/CPsIC67xuz6pLt6JhAM6Wg_pancreas-histology_english.jpg)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub
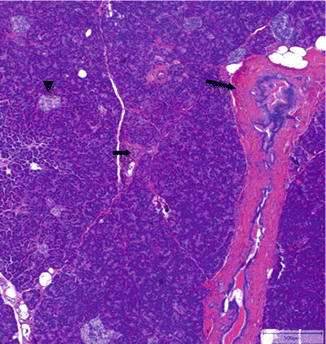



Histology Of The Pancreas Springerlink



Pancreas Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue




Histology Of Pancreas Youtube




Pancreas Histology




Pancreas Histology
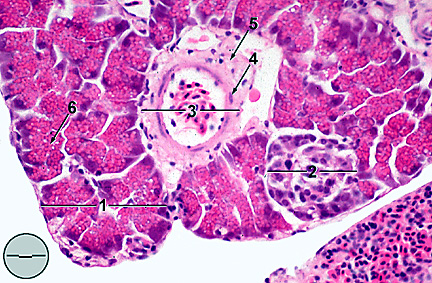



Digital Atlas Of Fathead Minnow Histology Digestive System Visceral Organs
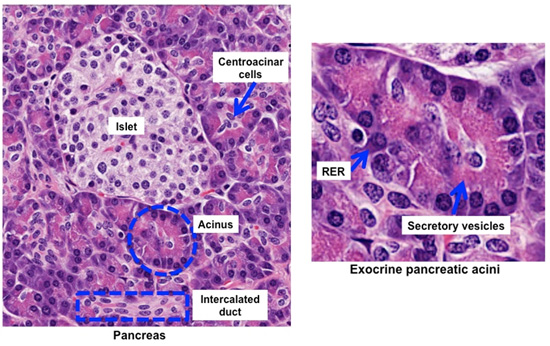



Human Structure Virtual Microscopy




Pancreas Histology Pancreas Labels Histology Slide Medical School Studying Histology Slides Medical Education
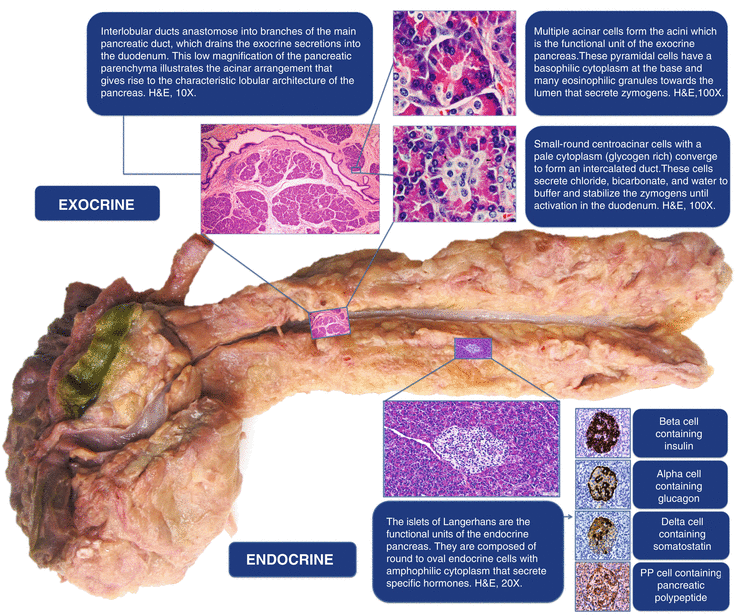



Histology Of The Pancreas Springerlink




Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas Pancreapedia
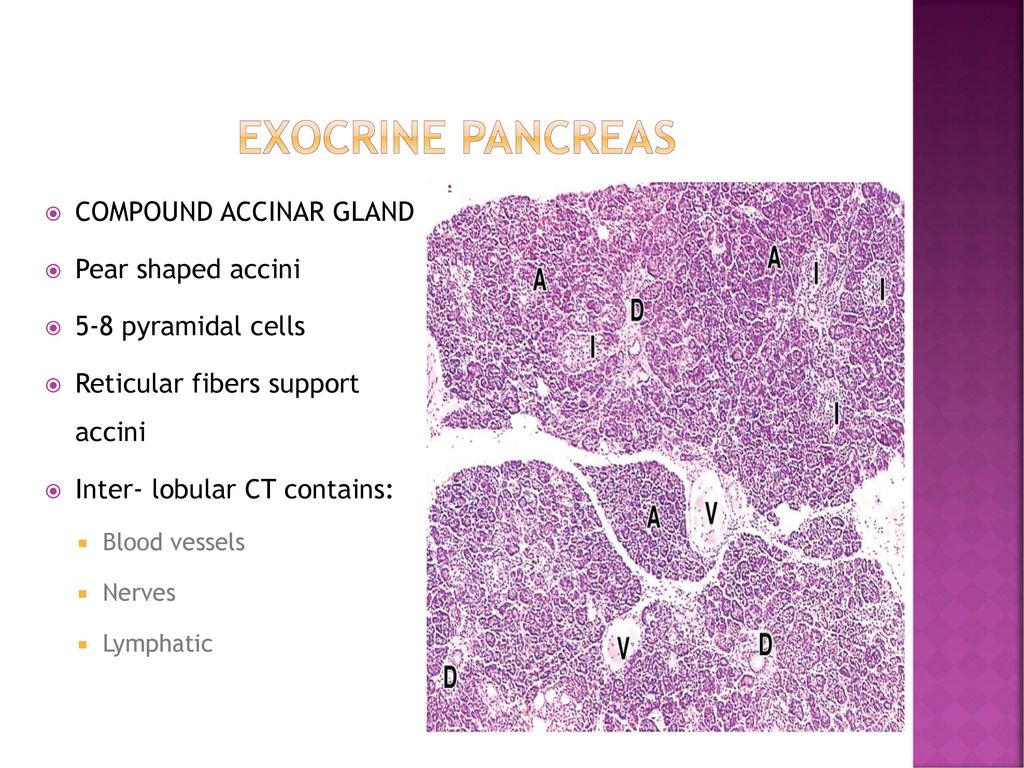



Histology Of Pancreas Ppt Download




Histology Of The Pancreas Endocrine And Exocrine Youtube
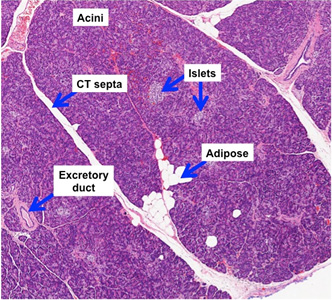



Human Structure Virtual Microscopy



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿